What is UV radiation and how to protect yourself from it?
UV radiation; there's a lot of confusion about it. What is exactly? And do you have to worry about it? In this blog we will give you a brief and powerful explanation and answer the most frequently asked questions:
- What is UV radiation?
- What is the difference between UVA, UVB and UVC?
- How much radiation is there in the Netherlands?
- What about UV radiation and sunbeds?
- What is the best way to protect yourself from UV radiation?
- Who needs to be extra careful with UV radiation?

1: What is UV radiation?
UV radiation is the invisible radiation of the sun. It is the rays that can cause sunburn, skin ageing and skin diseases when exposed to the sun excessively. Combustion is not caused by the sun's perceptible heat, but by the invisible radiation. That's why you don't only burn at 35 degrees Celsius during summer holidays, but also at -15 degrees Celsius in winter.
UV stands for UltraViolet radiation. It's an electromagnetic radiation that we just can't see with the human eye. The meaning is literal: beyond the violet, which is a reference to the wavelength of the radiation. An excess of ultraviolet radiation is harmful to the skin. UV radiation consists of three different types of radiation: UVA rays, UVB rays and UVC rays.
2: What is the difference between UVA, UVB and UVC?
UVA radiation
UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and are responsible for skin ageing. The A in UVA therefore stands for Ageing. Over-exposure to UVA can cause melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. UVA passes through glass, clouds and normal clothing. People, and especially children, who still have delicate skin, are therefore not protected if they wear only a T-shirt outdoors.
Most sun creams also do not or not fully protect against UVA rays, but they do protect against UVB rays. The UVA label on a bottle of sunscreen only means that at least one third of the factor protects against UVA.UV protective clothing does stop UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays have no immediate visible effect on the skin like UVB rays. For example, you can easily be over-exposed to UVA rays without being aware it.
UVB radiation
UVB radiation is the best known type of UV radiation. These are the rays that are responsible for tanning and reddening of the skin. UVB rays can also cause skin cancer, although there are several other, less aggressive forms of skin cancer than melanoma. Sunscreens contain fabrics that protect against UVB rays and also protect UV-resistant clothing against UVB rays.
UVC radiation
UVC radiation is lethal to us but fortunately it is completely blocked by the atmosphere and therefore has no effect on our skin. See image below:
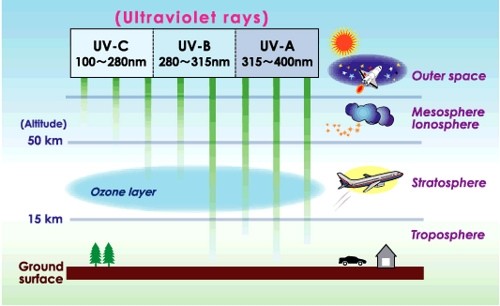
3: How much UV radiation is their nowadays in the Netherlands?
If you want to know the expected UV radiation today or this week, you can check various websites and weather institutes such as KNMI, weeronline and buienradar. The amount of UV radiation is expressed in terms of solar power and a UV index is made from that. In the Netherlands, the solar force can vary from 1 (very low) to 8 (maximum).
4: How about UV radiation and sunbeds?
If you use a sunbed, your skin is exposed to a large amount of UV radiation in a short period of time. The risk of skin cancer is therefore higher than under the 'normal' sun.
In addition, sunbeds mainly emit UVA and a very small amount or even no UVB. So you won't get sunburnt very quickly, but the rays penetrate deeper into your skin and cause it to age and increase the risk of skin diseases.

5: What is the best way to protect yourself against UV radiation?
UV radiation is the most preventable main cause of all forms of skin cancer. The best way to protect yourself against UV rays is to stay out of the bright sun and wear UV protective clothing when you are exposed to sunlight. An ordinary, dry white T-shirt only protects you with a SPF between 5 and 15, while UV protective clothing from UV-Fashions protects you with SPF50+. Other not so good UV protective clothing can protect your skin with SPF30. You can also give your own clothes a protection factor of 50+ by using the UV wax additive.
Furthermore, we recommend buying good UV sunglasses and a good protective hat, cap or sun visor from reliable top brands such as Dorfman Pacific, Rigon Headwear or Scala. It is also important to apply reliable, effective sunscreen. Want to know which sunscreen and which SPF you need? Read our blog with tips on sunscreen lubrication.
6: Who needs to be extra careful with UV radiation?
Children up to the age of 16 are particularly sensitive to UV radiation. Research has shown that children who god bad sunburns as a child have an increased risk of skin cancer later in life. In addition, it has been shown that skin cancer mainly affects people with a light skin type. Do you have a light skin type and do you often go out in the sun?
- Wear UV protective clothing;
- Apply sunscreen well and regularly;
- Check the skin for conspicuous and different coloured spots and lumps;
- When in doubt, go to the doctor.
Other people who need to be careful with UV radiation are chemotherapy patients, people with sun allergies, skin diseases and people taking certain medications. Want to read more about UV protection? Read my other blog here.




